Case by Dr. Enzo Attanasio
The selection of the restorative material is a crucial step in prosthodontics. Hybrid ceramics offer a range of properties well-suited for various therapeutic situations, both in the presence of vital teeth and of endodontically treated teeth. Using the example of a clinical case, this article will explore the advantages associated with the use of hybrid ceramics in a cracked tooth syndrome scenario.
INITIAL SITUATION
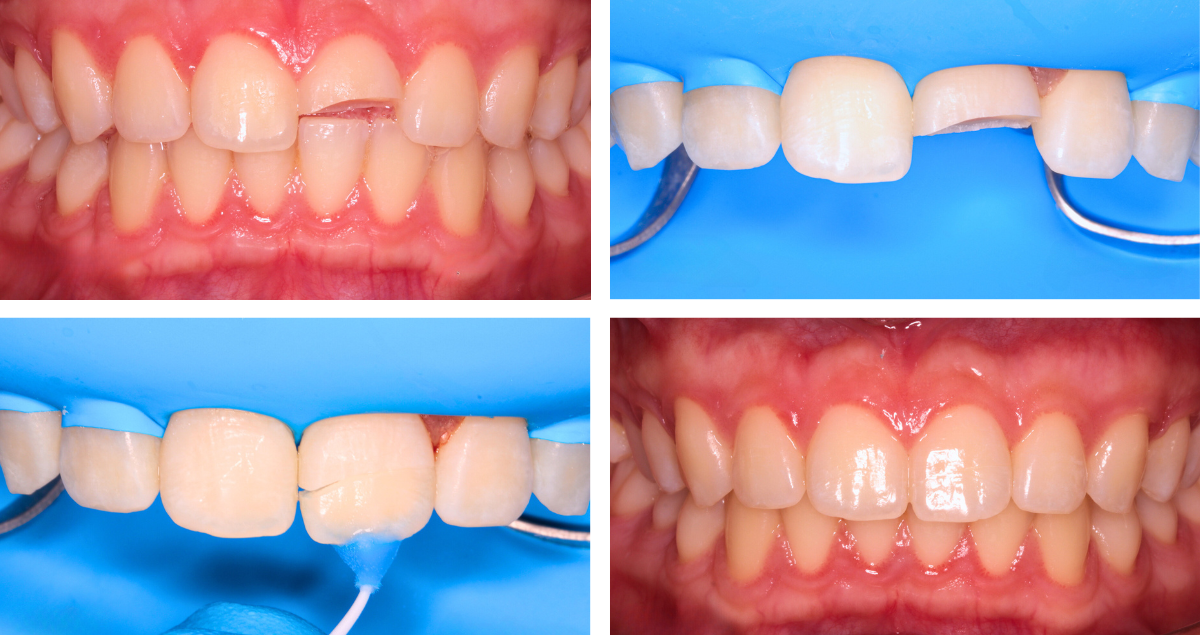
The affected tooth in this case was a mandibular right second premolar (45 according to the FDI notation) with an old amalgam restoration (Figs. 1 and 2). The patient experienced pain upon chewing (specifically upon release). Clinically, there were visible horizontal and vertical crack lines. The tooth was vital and showed no signs of pulpal pathology. It was decided to replace the amalgam restoration and restore the tooth with an overlay made of the hybrid ceramic KATANA™ AVENCIA™ Block. There were two main reasons for this decision. First, whenever root canal treatment would be necessary in the future, the hybrid ceramic material would facilitate endodontic access cavity preparation (compared to any other ceramic material) and subsequent restoration with composite filling material. Second, hybrid ceramics offer greater resistance and improved mechanical properties compared to composite filling materials applied in an incremental layering technique.
Fig. 1. Initial situation: Occlusal view.
Fig. 2. Initial situation: Buccal view.
PREPARATION AND IMMEDIATE DENTIN SEALING
To remove the amalgam restoration and weakened surrounding tooth structure, the occlusal surface of the tooth was reduced by approximately 2 mm. For a smooth colour transition between the tooth and the restoration, the preparation outline was created at the level of interproximal boxes with a vestibular inclined plane (Fig. 3). Subsequently, Immediate Dentinal Sealing (IDS) was carried out (Figs. 4 to 10). This technique involves the use of a universal adhesive like CLEARFIL™ Universal Bond Quick, which is applied to the preparation without prior etching of the peripheral enamel. In the second step, a highly filled flowable composite is applied. In the present case, the material of choice was CLEARFIL MAJESTY™ ES Flow Super Low, applied in a thickness of just 0.5 mm. The preparation was refined using ultrasonic instrumentation: Sonic tips SFM7 and SFD7 (Komet Dental) for refining the boxes; SFD1F and SFM1F (Komet Dental) for margins and steps. Sharp edges were rounded with abrasive discs and then polished with fine polishers. It is crucial that the residual occlusal thickness (prosthetic space) is 1.5 mm, as required by the selected material.
Fig. 3. Prepared tooth structure prior to immediate dentin sealing.
Fig. 4. IDS: Application of the universal adhesive.
Fig. 5. IDS: Light curing of the adhesive layer.
Fig. 6. Thin layer of flowable composite applied to the preparation.
Fig. 7. Contouring, …
Fig. 8. … rounding off sharp edges …
Fig. 9. … and polishing of the sealed surface with dedicated instruments.
Fig. 10. Sealed tooth preparation ready for impression taking.
FROM SCANNING TO TRY-IN
Following digital scanning with the intraoral scanner Primescan™ (Dentsply Sirona), MDT Daniele Rondoni produced the restoration (Figs. 11 and 12). The cementation process involves an initial try in phase to assess the marginal fit of the overlay and the contact areas. Testing occlusion at this stage could be risky as it may lead to fracture of the restoration in case of excessive premature contacts. After try-in (when carried out without rubber dam), the restoration may be contaminated by blood, saliva, or glycerin gel used for the evaluation of fit and aesthetics. Therefore, it is necessary to clean the restoration before proceeding with adhesive phases. The use of a cotton pellet soaked in alcohol is an option, a cleaning agent like KATANA™ Cleaner may be even better as it chemically cleans the restoration and eliminates the contaminants.
Fig. 11. Hybrid ceramic overlay on the printed model.
Fig. 12. Separate overlay.
CONDITIONING OF THE TOOTH AND THE RESTORATION
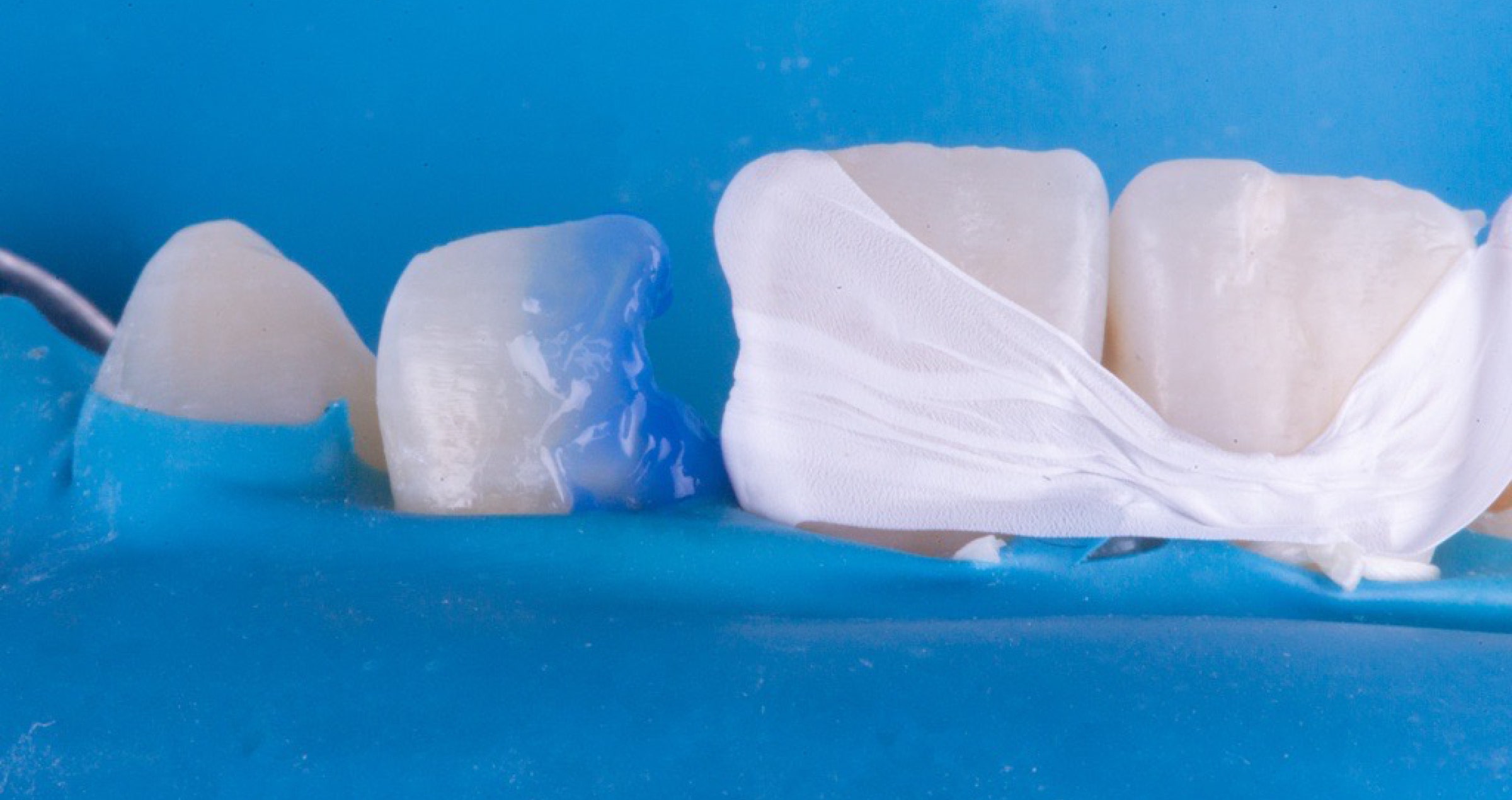
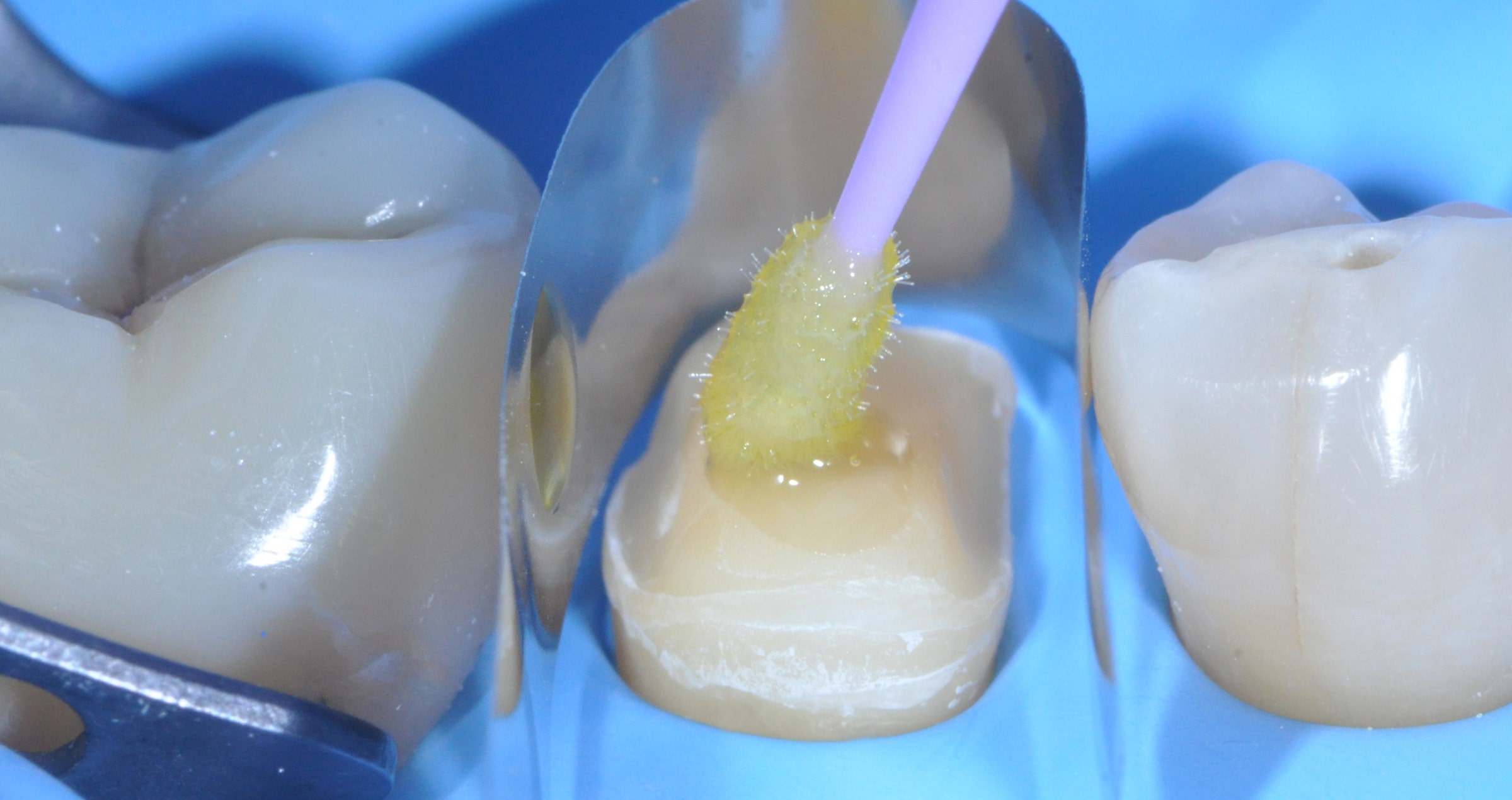
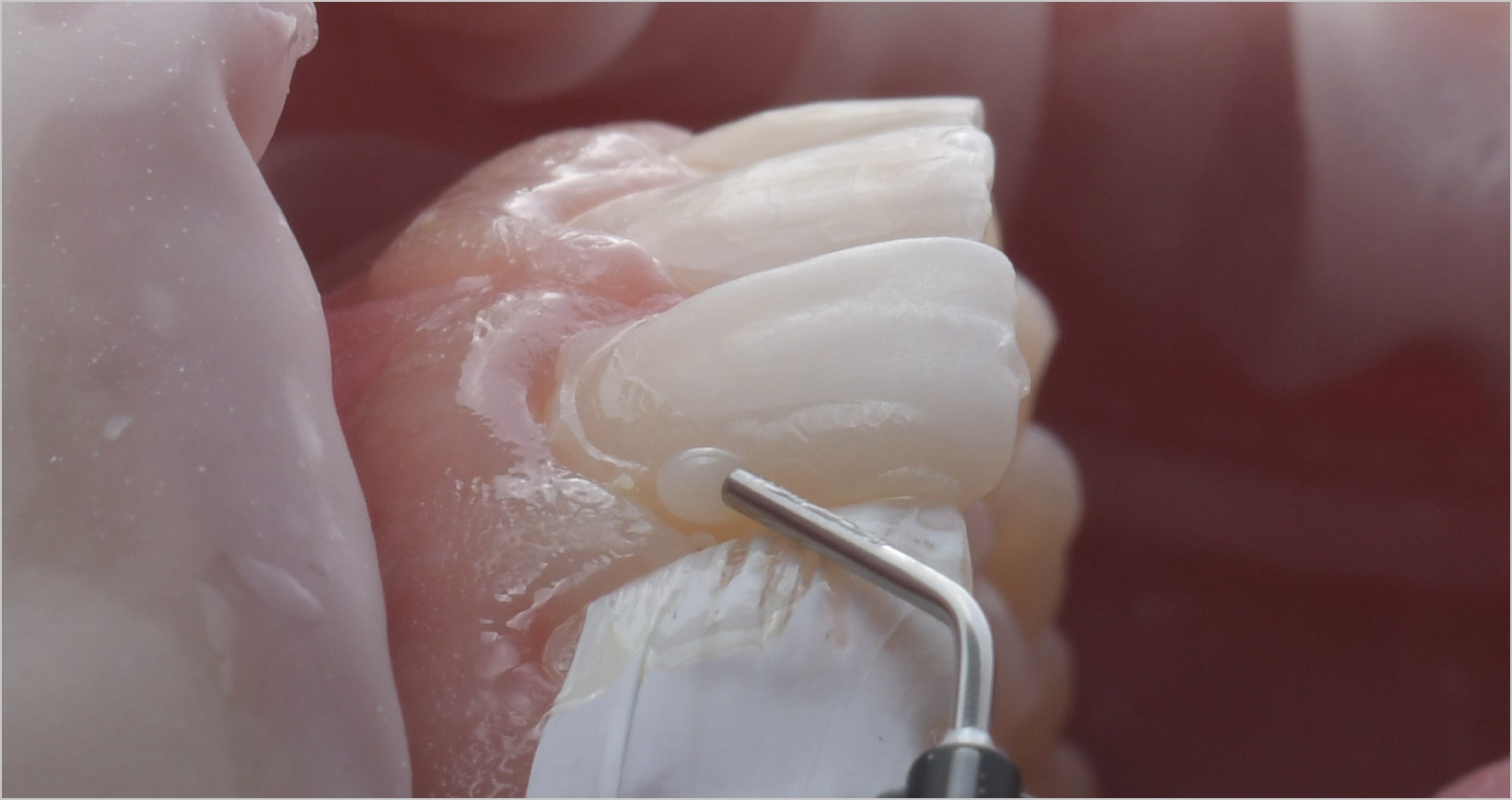
Afterwards, the restoration was sandblasted (as recommended for most hybrid ceramics) with 50 μm aluminum oxide using AquaCare (Akura Medical) (Fig. 13), and then immersed in distilled water in an ultrasonic bath for 5 minutes. Meanwhile, rubber dam was placed over the entire sextant, the build-up was sandblasted like the intaglio of the overlay and a phosphoric acid etchant (Ultra Etch, Ultradent) was applied to the enamel, rinsed off and the area dried (Figs. 14 to 17). The clean restoration was subsequently conditioned with a silane containing 10-MDP (CLEARFIL™ Ceramic Primer Plus, Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc.) according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Fig. 18). What followed was the application of the universal adhesive (CLEARFIL™ Universal Bond Quick) to the intaglio of the overlay and to the preparation and light curing on both sites (Figs. 19 and 20). One of the advantages of universal adhesives compared to three-step adhesive systems is their minimal film thickness, which does not compromise the fit of the restoration.
It is important to protect adjacent teeth with metal matrix strips during adhesive phases to provide for proper fitting. These elements do not create operational difficulties, but serve their purpose: After restoration placement, the composite or cement used for placement will be easily removable from the mesial and distal surfaces of the adjacent teeth, as they are free of adhesive.
Fig. 13. Sandblasting of the overlay …
Fig. 14. … and the tooth structure.
Fig. 15. Selective etching of the enamel, …
Fig. 16. … followed by thorough rinsing. Adjacent teeth are protected by a metal matrix strip.
Fig. 17. Tooth structure after selective etching, rinsing and drying.
Fig. 18. Silane application.
Fig. 19. Application of the universal adhesive into the overlay.
Fig. 20. Treatment of the tooth structure with the universal adhesive.
DEFINITIVE PLACEMENT
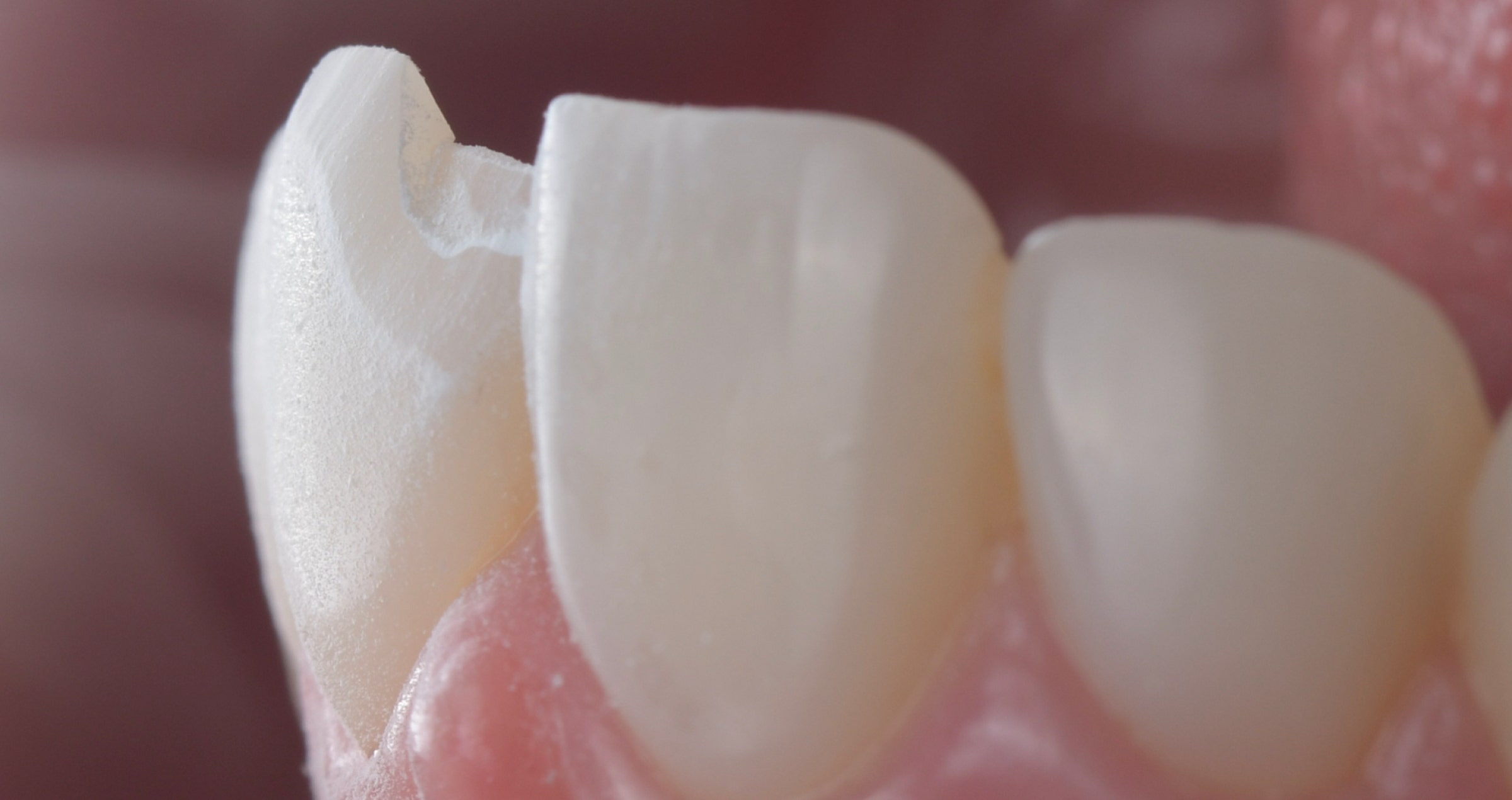
In the present case, a heated composite paste (heated to a temperature of 55 °C) was extruded into the restoration, which was then placed by applying slow, gradual, and strong pressure (Figs. 21 and 22). Excess composite was removed with a scaler in the buccal and lingual areas and floss (e.g. SuperFloss®, Oral-B) in the interproximal areas. Several pressurization phases were performed until no more composite was observed at the tooth-restoration interface.
Fig. 21. Heated composite paste used for definitive placement.
Fig. 22. Restoration placed under rubber dam isolation.
Then, the composite was polymerized for 30 seconds from the buccal and lingual sides with two curing lights, before applying glycerin gel to the margins and polymerizing from occlusal for another minute (Fig. 23). If thorough attention is given to removing excess composite during placement phases, subsequent finishing steps will be quick and easy (Figs. 24 to 27). Finishing and polishing of the interproximal areas was accomplished with an EVA handpiece and 3M™ Sof-Lex™ Finishing Strips (3M). For finishing of the buccal and lingual areas, a medium-grit, flame-shaped diamond bur (diameter 14/16) was used. Finally, the margins should be polished using composite polishers like TWIST™ DIA for Composite (Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc.). After the local anesthesia wears off, one should observe the cessation of pain symptoms, as seen in the present case. The treatment outcome is displayed in Figures 28 and 29.
Fig. 23. Light curing through a layer of glycerin gel blocking the oxygen.
Fig. 24. Finishing of the buccal and lingual margin with a medium-grid, flame-shaped diamond bur.
Fig. 25. Finishing of the interproximal areas with EVA handpiece (fine grain).
Fig. 26. Checking the occlusal contacts.
Fig. 27. Occlusal polishing.
FINAL SITUATION
Fig. 28. Treatment outcome – buccal view.
Fig. 29. Treatment outcome – occlusal view.
CONCLUSION
For posterior teeth restored with amalgam and a significant level of destruction, restoration replacement with hybrid ceramic overlays can be a great option. Mechanical material properties are usually superior to those of layered composites, processing is possible chairside or labside and comparatively quick (no firing required), while the clinical placement procedure is similar to that involved in placing glass ceramics – with the major difference of sandblasting instead of etching the intaglio of the restoration. One of the most important benefits of hybrid ceramics over glass ceramics, however, is the ability to modify the restoration whenever desired. Endodontic access cavities are easily prepared and closed with composite, contact points are quickly adjusted and the surface is polished or re-polished in next to no time. Moreover, the wear properties are similar to those of tooth structure and patients are happy about a natural touch and feel. The aesthetic properties are quite impressive, too.
Dentist:
ENZO ATTANASIO
Enzo Attanasio graduated in 2008 in Dentistry and Dental Prosthetics from the Magna Graecia University of Catanzaro. In 2009, he went on to specialize in the use of laser and new technologies in the treatment of oral and perioral tissues at the University of Florence. That year he also attended Prof. Arnaldo Castellucci’s course in Clinical Endodontics at the Teaching Center of Microendodontics in Florence where, in 2012, he went on to complete his training in Surgical Microendodontics. In 2017 he attended a course on Direct and indirect Adhesive Restorations at Prof. Riccardo Becciani’s Think Adhesive training center in Florence where he later become a tutor. Today, as a member of the Italian AIC and based in Lamezia Terme, Italy, Dr Attanasio has a special interest in Endodontics and Aesthetic Conservative.