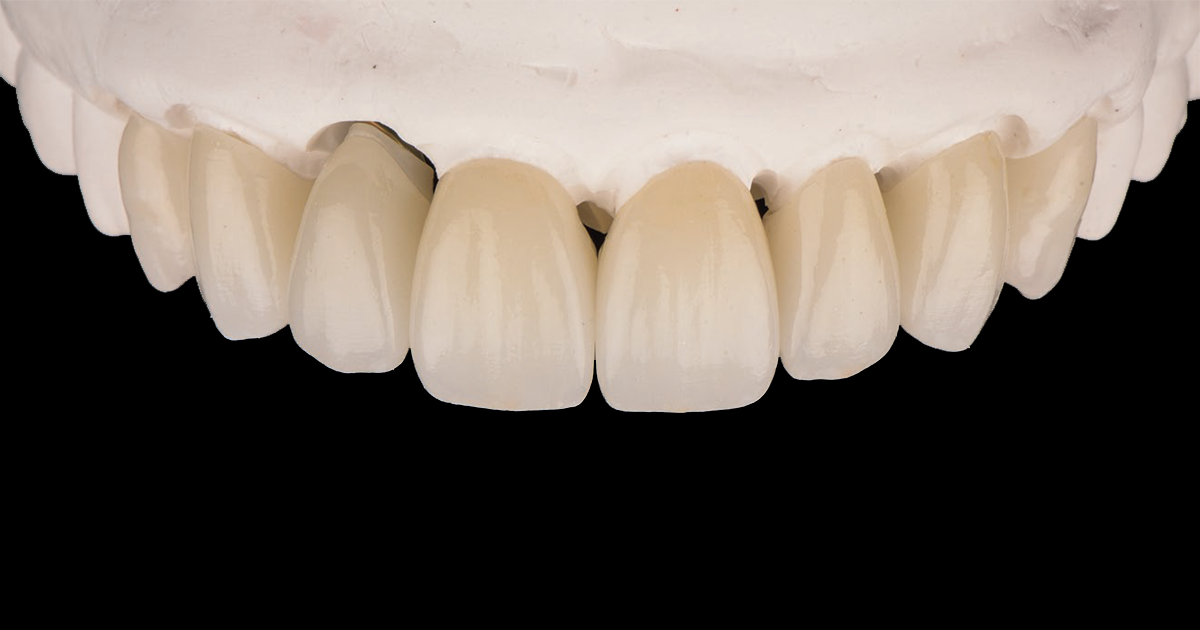
KATANA™ Zirconia STML is a highly popular material used in many dental laboratories around the world. Compared to traditional zirconia framework materials with a mainly tetragonal polycrystalline structure, the material has a higher yttria content, leading to a different material structure with an impact on the optical and physical properties (the translucency is increased, the flexural strength reduced). As a consequence, the indication range is limited to single-tooth restorations and two to three-unit bridges in the anterior and posterior regions. The greatest benefit lies in a much higher aesthetic potential, which is responsible for the fact that the material is predominantly used for the production of monolithic restorations or those with a micro cut-back individualized with a micro-layer of porcelain.
While the indications and technical procedure are wellknown, there seem to be some obscurities regarding the handling in the dental office. Is conventional cementation possible and recommended or is an adhesive luting procedure preferable? Is the surface pre-treatment the same as for tetragonal zirconia or is a different procedure required? And what may be expected regarding the longterm behaviour of KATANA™ Zirconia STML restorations? A close look into the available scientific literature provides some guidance.
DEFINITIVE PLACEMENT OF RESTORATIONS MADE OF KATANA™ ZIRCONIA STML
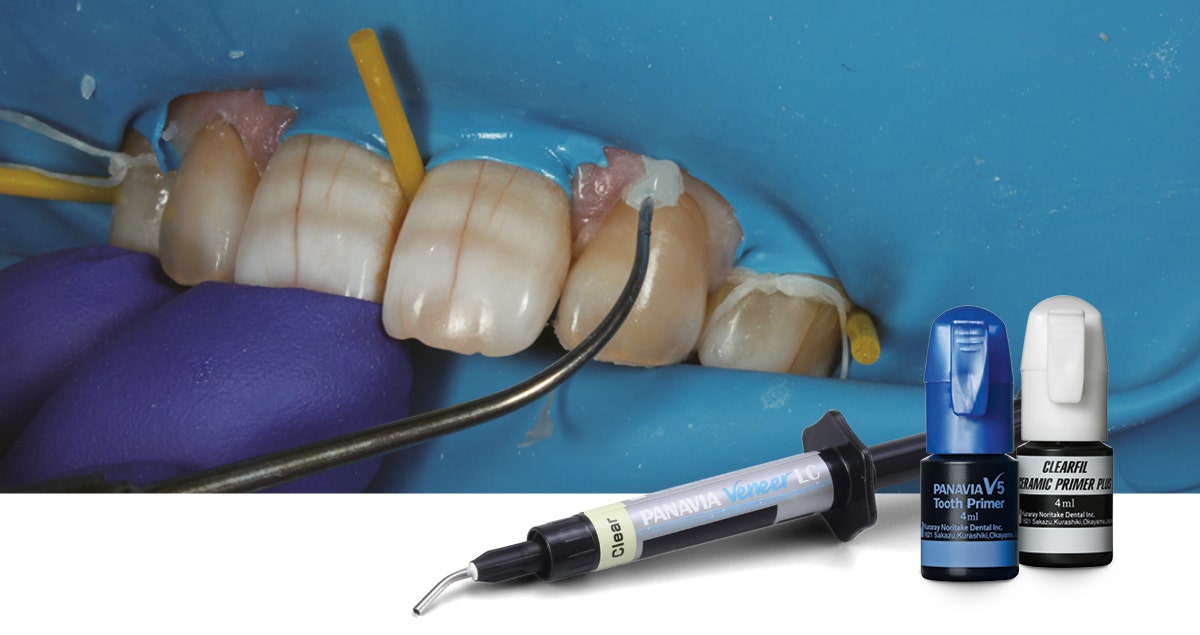
Conventional cementation or adhesive luting? In principle, both procedures are possible when the restoration to be placed has a retentive design. It is generally accepted that a full coverage crown provides sufficient retention for conventional cementation when the abutment tooth is at least 4 mm high and the convergence angle of the axial walls ranges between 6 and 12 or maximally 15 degrees (1,2). The reason is that the flexural strength of the material is higher than 350 MPa (3), the critical value for conventional cementation. As conventional cements are opaque and available in a single shade, however, the use of a (self-) adhesive resin cement may be preferable with all hightranslucency restorative materials for aesthetic reasons. Anyway, these products are mandatory whenever a macroretentive preparation design is not feasible or wanted. To sum up, the use of a self-adhesive or adhesive resin cement is preferable in many situations. An argument in favour of self-adhesive resin cements is the lower effort involved in their use. But what about the pre-treatment of the zirconia? No matter what type of dental zirconia is used, etching with hydrofluoric acid is ineffective due to the lack of glass matrix in the material. However, it is clear that surface modification is necessary to establish a strong and durable bond to any resin cement system4,5. The method generally recommended for high-strength zirconia is sandblasting with aluminium oxide particles or tribochemical silica coating4. The particle size should be small (≤ 50 μm) and the pressure low (about 1 bar) to avoid a weakening of the material’s mechanical properties (3,4). For lower-strength material variants, this risk of weakening the material seems to be higher (5), so that it becomes even more important to work with a low pressure and particle size (5-8). In the case of KATANA™ Zirconia, however, it was reported that “alumina-sandblasting significantly increased the biaxial flexural strength of KATANA™ STML.” (9) This means that proper sandblasting of restorations made of KATANA™ Zirconia STML did not affect the flexural strength of the material, which was even increased because of the specific properties of zirconia from Kuraray Noritake Dental.
Based on these findings, the following procedures are recommended for high-translucency zirconia:
OPTION 1
Aluminium oxide air-abrasion followed by the use of a selfadhesive resin cement containing 10-MDP (6)
OPTION 2
Tribochemical silica coating followed by silanization of the bonding surface (6)
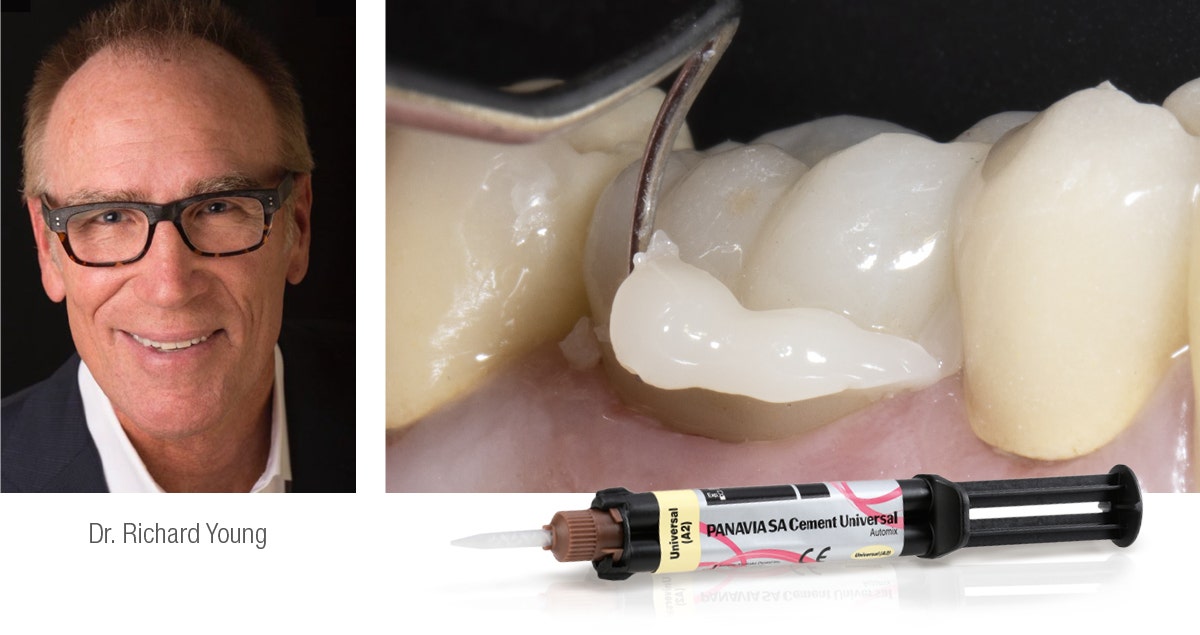
As the dual-cure self-adhesive resin cement PANAVIA™ SA Cement Universal contains the Original MDP monomer and the long carbon-chain silane coupling agent (LCSi Monomer), it is suited for both procedures. PANAVIA™ SA Cement Universal is available in an automix syringe and a handmix system, which consist of a pastepaste formulation. One paste contains the Original MDP monomer in a hydrophilic monomer environment and the other contains the inactive LCSi Monomer in an environment of hydrophobic monomers. When extruding the pastes, they are mixed in the syringe’s mixing tip (automix) or dispensed on a mixing pad and mixed by hand (handmix). Afterwards, the material is simply applied to the intaglio of the restoration and the restoration is placed. Cleanup of excess cement is easiest after tack-curing (2 to 5 seconds).
DOES THIS WORK WELL IN THE CLINICAL ENVIRONMENT?
The best way to check whether the described procedure is successful in the clinical environment is by conducting a clinical study. This is exactly what a group of researchers from the University Complutense of Madrid, Spain, has done with the material combination KATANA™ Zirconia STML and PANAVIA™ SA Cement Universal (10). Within the framework of the prospective clinical trial, 30 posterior crowns made of KATANA™ Zirconia STML were placed in 24 individuals in need of posterior tooth restorations. The teeth were prepared as recommended for all-ceramic restorations, allowing for a wall thickness of approximately 1 mm (recommended minimum wall thickness of KATANA™ Zirconia STML for crowns in the posterior region: 1.0 mm). The restorations were sintered, characterized and glazed as recommended by the material manufacturer and subsequently tried in. Prior to cementation, the intaglio of the restorations was pre-treated with aluminium oxide particles (50 μm, 1 bar pressure) followed by ultrasonic cleaning. The use of PANAVIA™ SA Cement Universal also was in line with the manufacturer’s recommendations. A clinical evaluation of the crowns was performed after 6, 12 and 24 months using the California Dental Association (CDA) quality evaluation system. The parameters evaluated in this system are the surface and colour of the restorations, their anatomical form and the marginal integrity of the crowns. After 24 months, the success and survival rates were 100 percent. Regarding all three parameters, the crowns received a “satisfactory” (Score 3 or 4) rating, marginal integrity (the key parameter to judge the performance of the resin cement) received an “excellent (the highest possible Score 4) in all 30 cases.
CONCLUSION
The researchers concluded that “the excellent results obtained in this study suggest that the third-generation tooth-supported monolithic zirconia crowns in posterior regions seem to be a good alternative to metal-ceramic crowns, second-generation monolithic zirconia crowns, and veneered zirconia crowns. A long-term study is necessary to confirm this short-period study.” Hence, it seems that KATANA™ Zirconia STML and PANAVIA™ SA Cement Universal are a promising team, and that adhering to the recommended abovementioned protocols is likely to produce excellent results that are stable over many years.
References:
1 Edelhoff D, Özcan M. To what extent does the longevity of fixed dental prostheses depend on the function of the cement? Working Group 4 materials: cementation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007;18 Suppl3:193-204. 2 Güth JF, Stawarczyk B, Edelhoff D, Liebermann A. Zirconia and its novel compositions: What do clinicians need to know? Quintessence Int. 2019;50(7):512-20. 3 Kern M, Beuer F, Frankenberger R, Kohal RJ, Kunzelmann KH, Mehl A, Pospiech P, Reis B. All-ceramics at a glance. An introduction to the indications, material selection, preparation and insertion techniques for all-ceramic restorations. Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Keramik in der Zahnheilkunde. 3rd English edition, January 2017. 4 Comino-Garayoa R, Peláez J, Tobar C, Rodríguez V, Suárez MJ. Adhesion to Zirconia: A Systematic Review of Surface Pretreatments and Resin Cements. Materials (Basel). 2021 May 22;14(11):2751. 5 Mehari K, Parke AS, Gallardo FF, Vandewalle KS. Assessing the Effects of Air Abrasion with Aluminum Oxide or Glass Beads to Zirconia on the Bond Strength of Cement. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2020 Jul 1;21(7):713-717. 6 Chen B, Yan Y, Xie H, Meng H, Zhang H, Chen C. Effects of Tribochemical Silica Coating and Alumina-Particle Air Abrasion on 3Y-TZP and 5Y-TZP: Evaluation of Surface Hardness, Roughness, Bonding, and Phase Transformation. J Adhes Dent. 2020;22(4):373-382. 7 Alammar A, Blatz MB. The resin bond to high-translucent zirconia-A systematic review. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2022 Jan;34(1):117-135. 8 Soto-Montero J, Missiato AV, dos Santos Dias CT, Giannini M. Effect of airborne particle abrasion and primer application on the surface wettability and bond strength of resin cements to translucent zirconia. J Adhes Sci Technol, Online publication May 2022. 9 Inokoshi M, Shimizubata M, Nozaki K, Takagaki T, Yoshihara K, Minakuchi S, Vleugels J, Van Meerbeek B, Zhang F. Impact of sandblasting on the flexural strength of highly translucent zirconia. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021 Mar;115:104268. 10 Gseibat M, Sevilla P, Lopez-Suarez C, Rodríguez V, Peláez J, Suárez MJ. Prospective Clinical Evaluation of Posterior Third-Generation Monolithic Zirconia Crowns Fabricated with Complete Digital Workflow: Two-Year Follow-Up. Materials (Basel). 2022 Jan 17;15(2):672. (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35057389/)