4 Clinical cases by Dr. Jusuf Lukarcanin
Composites with a universal shade concept, a reduced number of shades that may be selected without any shade guide are a clear trend in restorative dentistry. With specific blend-in properties, these materials can help streamline restorative procedures and reduce chair time, take some pressure off the dental practitioner and contribute to potentially good outcomes. Some users, however, are skeptical about a wide-scale use of the materials, particularly when it comes to restoring teeth in the anterior region. The reasons may be a comparatively high translucency requiring the separate application of a blocker (or opacious shade) in certain situations, or a too limited shade offering.
Personal experience shows that CLEARFIL MAJESTY™ ES-2 Universal is perfectly suitable for a wide range of single-shade restorations in anterior teeth. It offers great polishability and long-term gloss retention and is available in just four shades: One universal shade (U) originally designed for posterior restorations, universal light (UL) and universal dark (UD) as the two major options for anterior teeth and, finally, universal white (UW) for the imitation of any bleached shade. In general, all four options may be used in the anterior and posterior region. As the blend-in ability is due to proprietary light-diffusion technology and not managed via an increased translucency, the application of a blocker is usually not necessary and even larger areas can be restored quite inconspicuously.
For those asking themselves when to select which shade in the anterior region, the following clinical case examples and comments may provide some useful guidance. The recommendations and practical tips are based on personal experience. All patients were in treatment for diastema closure or shape correction, but the selection criteria are the same for other types of anterior restorations, too.
UNIVERSAL LIGHT: FOR NATURAL RESULTS IN BRIGHTER TEETH
This young patient aged 35 with microdontia presented in the dental office with the desire to have more beautifully shaped teeth. His teeth were almost free of dental caries, but with deficiencies in oral hygiene and signs of gingival inflammation. A deep bite was also evident. After professional tooth cleaning and oral hygiene advice, the teeth were restored with CLEARFIL MAJESTY™ ES-2 Universal in the shade UL.
Fig. 1. Initial situation.
Fig. 2. Initial situation: Deep bite.
Fig. 3. Teeth restored with composite in the single-shade technique.
Fig. 4. Immediate treatment outcome.
Reasons for selecting universal light:
- For younger patients (tooth shades A2 and lighter)
- Situations in which light easily passes through the composite (e.g., Class III, Class IV)
Universal light properties:
- High light scattering effect
- Well-balanced translucency
UNIVERSAL DARK: FOR NATURAL RESULTS IN DARKER TEETH
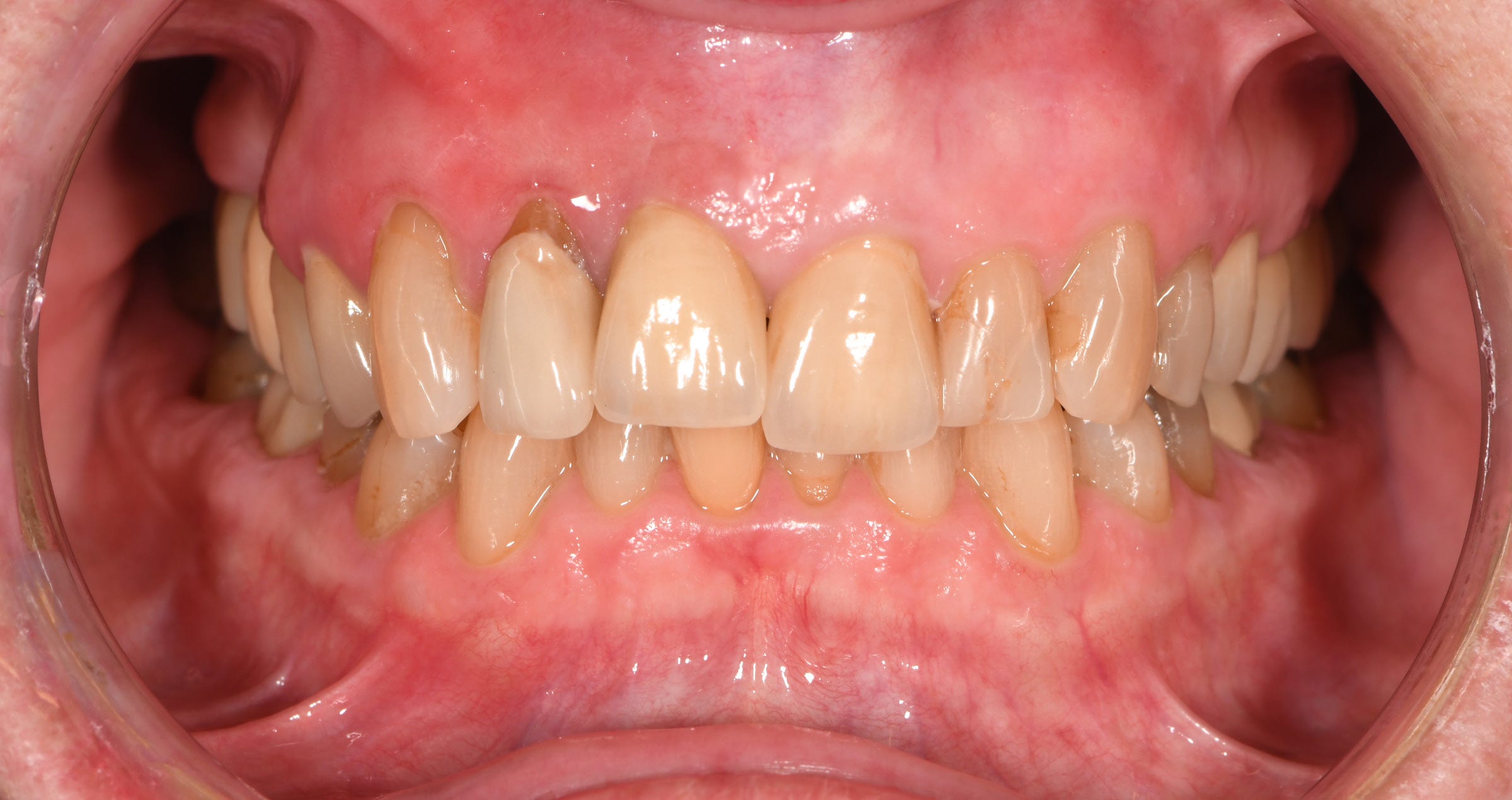
Abrasion and shape correction was also the major reason for this 58-year-old female patient to ask for cosmetic dental treatment. She was unhappy with the appearance of the anterior teeth in the maxilla, which showed signs of tooth wear and discolouration. The selected treatment approach was composite veneering with CLEARFIL MAJESTY™ ES-2 Universal in the shade UD. The shade was selected based on the indication and the somewhat darker shade of the patient’s natural teeth.
Fig. 1. Initial clinical situation.
Fig. 2. Treatment outcome.
Reasons for selecting universal dark:
- For older patients (tooth shades A3 and darker)
- Situations in which light easily passes through the composite (e.g., Class III, Class IV)
Universal dark properties:
- High light scattering effect
- Well-balanced translucency
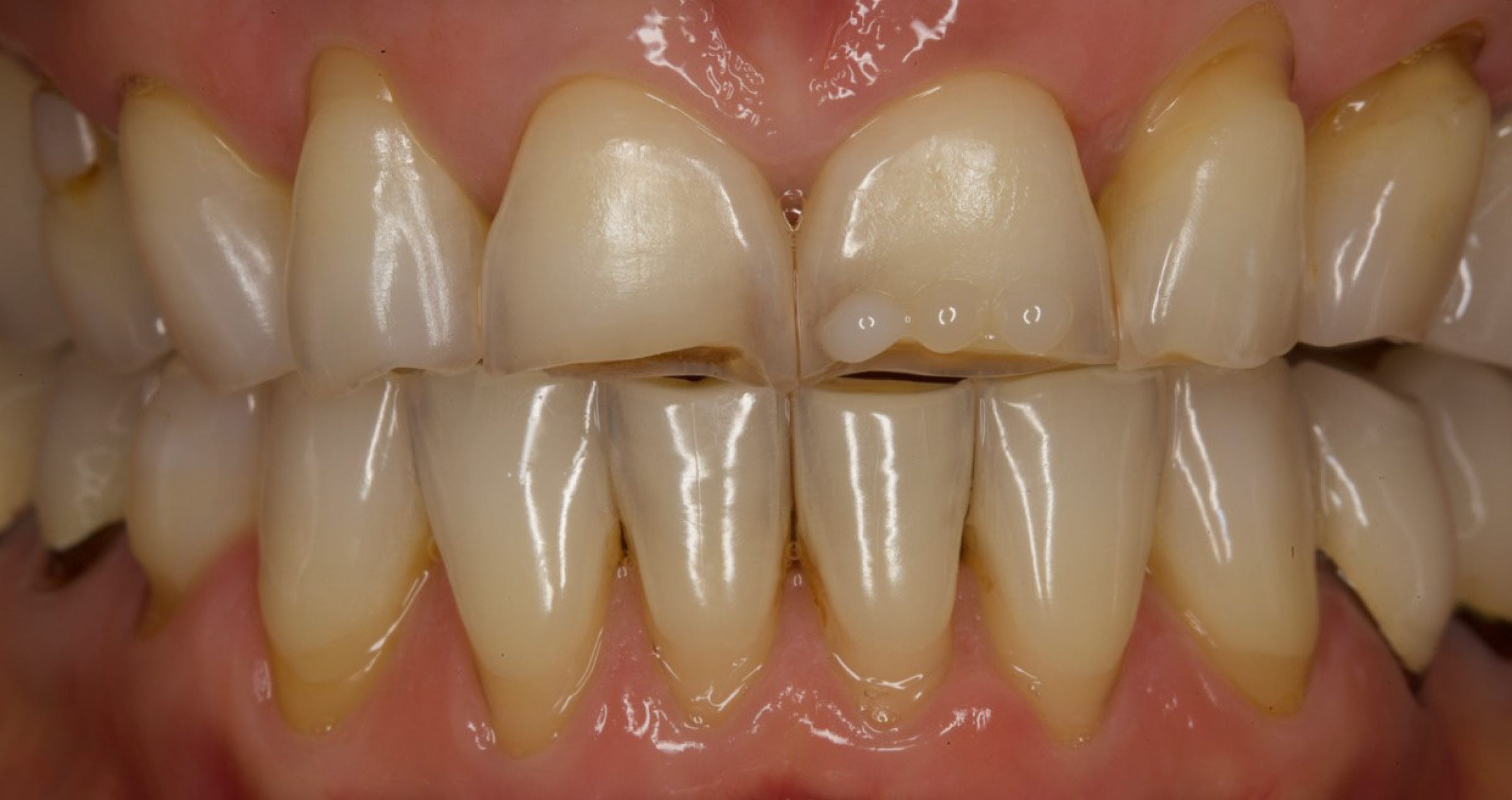
UNIVERSAL: WHENEVER A HIGH TRANSLUCENCY IS DESIRED
In teeth in which the areas to be restored are surrounded by a lot of non-discoloured tooth structure - as may be the case in Class I, II and Class V cavities - the use of CLEARFIL MAJESTY™ ES-2 Universal in the shade U may be an option. The 28-year-old patient, who presented for diastema closure, had teeth with a comparatively low translucency and different shades due to smoking and excessive coffee consumption. As the composite was applied in enamel areas only, the relatively high translucency of the universal shade seemed beneficial in this case.
Fig. 1. Initial clinical situation.
Fig. 2. New smile of the patient.
Reasons for selecting universal:
- Large amounts of underlying or surrounding tooth structure present
- Medium light-scattering desired
Universal properties:
- High translucency
- Medium light-scattering effect
UNIVERSAL WHITE: FOR ALL PATIENTS ASKING FOR A BLEACHED EFFECT
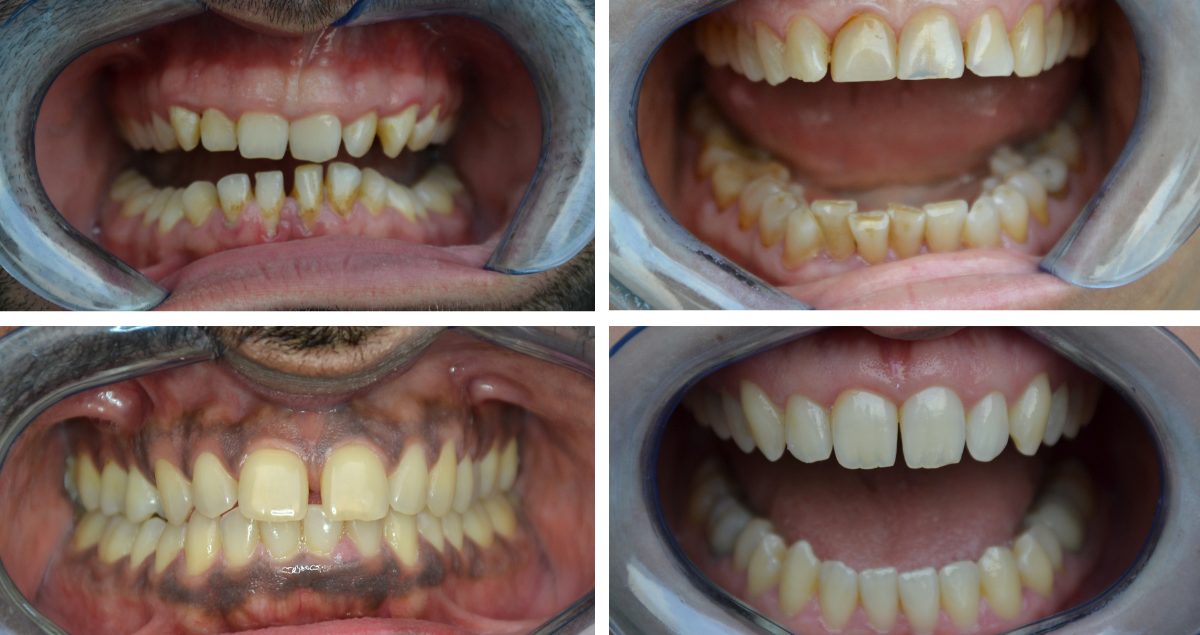
For all cases that require a particularly bright tooth shade – e.g. children or patients with bleached teeth / asking for a bleached effect in their restorations – CLEARFIL MAJESTY™ ES-2 Universal in the shade UW is likely to be the first choice. The young patient aged 28 shown below asked for diastema closure including shape and shade correction: She wanted to have a brighter, more beautiful smile.
Fig. 1. Initial clinical situation.
Fig. 2. Shape and shade correction were desired in this case.
Fig. 3. Treatment outcome …
Fig. 4. … leading to the beautiful smile the patient desired.
Reasons for selecting universal white:
- Cases requiring a particularly high brightness or value
- Restorations in deciduous teeth
- Restorations in bleached teeth
Universal white properties:
- Well-balanced translucency
- High light-scattering effect
CONCLUSION
One universal composite, four shades: In the case of CLEARFIL MAJESTY™ ES-2 Universal, this portfolio is absolutely sufficient for single-shade restorations even in the aesthetically demanding anterior region. Properties such as a nice blend-in effect, a great polishability and gloss retention over time support dental practitioners in creating beautiful restorations. As shade determination may be based on very few criteria instead of a complex shade guide, the whole restoration procedure becomes less stressful and more efficient. Furthermore, with only four shades to stock and usually no blocker needed, the number of materials on stock is reduced, leading to facilitations in stock management as well.
Dentist:
JUSUF LUKARCANIN
Dr. Jusuf Lukarcanin is a Certified Dental Technician (DCT) and a Doctor of Dental Science (DDS). He studied dentistry at the Ege University Dental Faculty in Izmir, Turkey, where he obtained a Master‘s degree in 2011. In 2017, he received a Ph.D. degree from the Department of Restorative Dentistry of the same university. Between 2012 and 2019, Dr. Lukarcanin was the head doctor and general manager at a private clinic in Izmir.
Between 2019 and 2020, he worked at Tinaztepe GALEN Hospital as a Restorative Dentistry specialist, between 2020-2022 he worked at MEDICANA International Hospital Izmir as a Restorative Dentistry specialist. Currently he is an owner of a private clinic for aesthetics and cosmetics in Izmir.