Blog
Zirconia, Oral scanner, feather edge preparation: the “winning triad”
The introduction of digital technology associated with the development of the latest zirconia materials offers the clinical and the dental technician a wide range of solutions to achieve aesthetics and function in a simple, predictable and above all conservative way. A further type of vertical preparation called "Minimally Invasive Vertical Preparation" has been introduced, applicable to numerous prosthetic clinical situations including cases of aesthetics. Minimally invasive vertical preparations, new type of zirconia and intraoral scanners represent a “winner triad” for today's prosthetic therapy.
ABOUT DR DAVIDE CORTELLINI
Graduated with honors in Dentistry at the University of Siena in 1992, wins the scholarship of the Italian Society of Periodontology (SIDP) for the year 1994-95. He therefore has the opportunity to attend the Department of Periodontology and Fixed Prosthesis of Prof. NP. Lang at the University of Bern in Switzerland, carrying out clinical and research activities. He obtained the title of "Doctor Medicinae Dentium" (D.M.D.) at the same University in 2000.
Author of scientific publications in international journals, he is an Active Member of the Italian Academy of Prosthetic Dentistry (AIOP). Active member of the International Academy of Digital Dentistry (IADDM). He lectures in Italy and abroad, and he owns his private practice in Riccione mainly oriented to digital, aesthetic and complex prosthetic rehabilitations.
Instructional videos - Episode 3 - KATANA - Sintering
EC Certificate of Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc. products
At Kuraray Noritake Dental Inc. we are proud that our products are being developed using innovative technologies, paying attention to detail and keeping in mind the needs of our customers.
We are committed to offering outstanding products that provide dental professionals with the flexibility for self-expression and creativity, adding value and delivering superb aesthetic results to each and every procedure.
Usability, simplicity and, of course, quality always in mind - providing dental professionals with materials that will make their daily practice stress free.
As a prove that our products meet the needs of dentists and lab technicians alike, we are happy to share with you the EC Certificates of Full Quality Assurance System that we have received from The Notified Body. Those can be downloaded below.
Chairside products
Labside products
Join Dr Michael Braian on the webinar focusing on the bonding procedure of monolithic Zirconia to Ti-base utilising PANAVIA V5 procedures.
ABOUT DR MICHAEL BRAIAN
Michael Braian, DDS, CDT, PhD is an international reference in the Digital Dentistry area as he has been working with technology in the dental field for almost 15 years. His professional profile combines every key aspect in dentistry as he is a Dentist, Certified Dental Technician and has a PhD in Digital Dentistry by Malmö University.
Clinical case - Single crown on 11
By Dr Alessandro Devigus
Close up of insufficient crown on tooth 11.
After removal of old crown – discolored stump (endo treatment).
Try-in of the crown after sintering – no intrinsic fluorescence.
Try-in of the crown after glazing.
Try-in of the crown after glazing under cross polarized light to check the shade match.
Try-in of the crown after staining under cross polarized light to check the shade match.
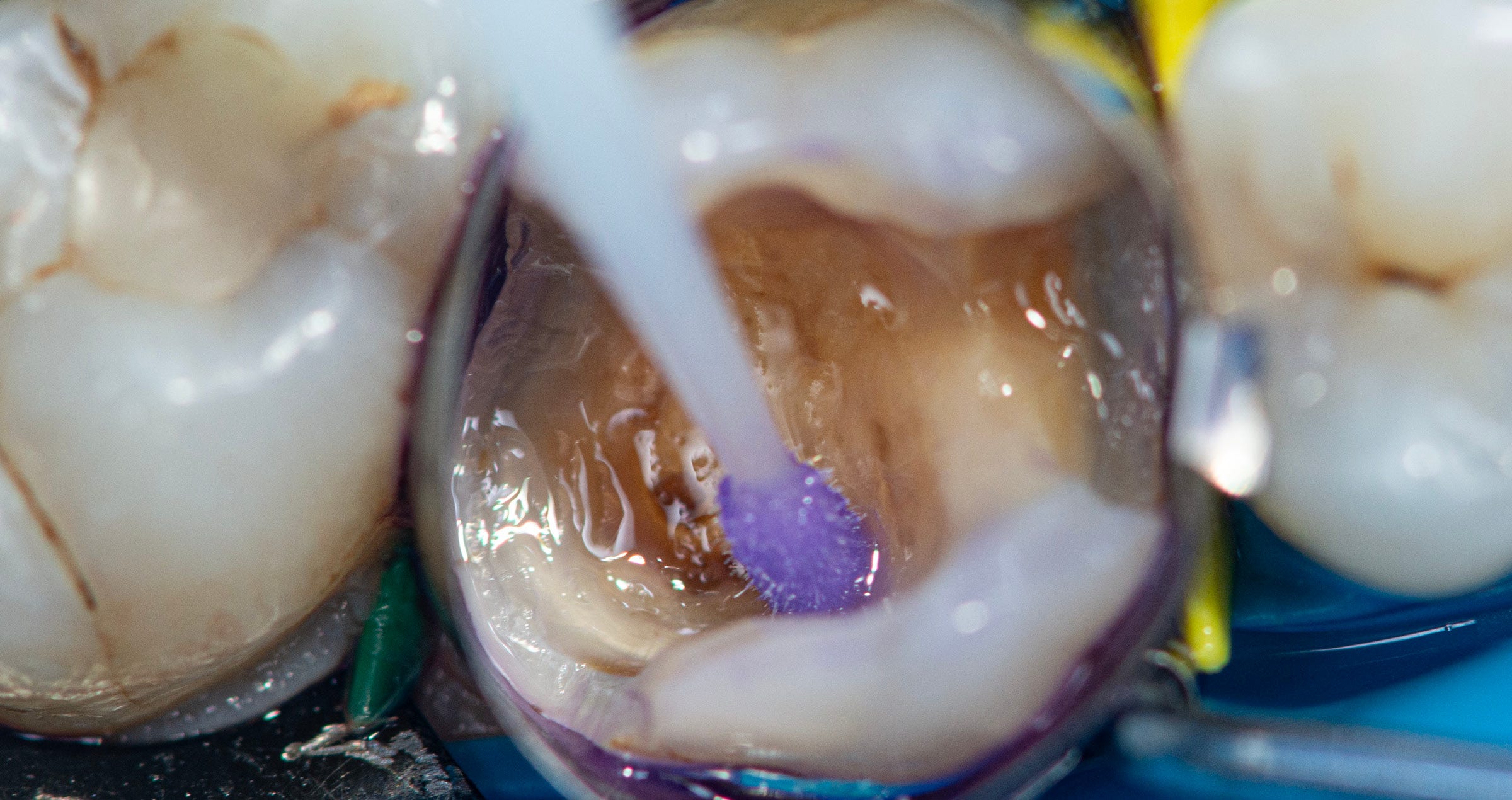
Retraction cord in situ for adhesive cementation with PANAVIA™ V5.
Adhesive cementation using PANAVIA™ V5 opaque to mask dark stump.
Control after 1 week.
Control after 1 week – cross polarized light to check shade.
Control after 1 week – fluorescence check.
FINAL SITUATION
Dentist:
Dr Alessandro Devigus received his degree from Zurich University, Switzerland, in 1987. Since 1990 his working in his own private practice with a focus on CAD CAM and Digital Dentistry. He is also CEREC Instructor at the Zurich Dental School.
Dr Alessandro Devigus is an active member of the European Academy of Esthetic Dentistry (EAED), founder of the Swiss Society of Computerized Dentistry, Neue Gruppe member, ITI fellow and speaker.
Dr Devigus is editor-in-chief of the International Journal of Esthetic Dentistry, author of various publications and an international lecturer.
KATANA™ Zirconia: The complete restorative solution
When it was first introduced to restorative dentistry in the early 2000s, zirconia was an opaque, unnatural-looking substance with a chalk-like whiteness. Two decades later, technological and material advances have meant that zirconia is now a highly aesthetic and durable ceramic solution for a variety of procedures. Leading the way is Kuraray Noritake Dental’s KATANA™ Zirconia series, which can now be integrated at every step of the restorative workflow.
The pioneering nature of KATANA™ Zirconia
Key reasons for zirconia’s improvements as a dental material are continued innovations in the powder that forms the basis of the discs. While a majority of dental zirconia manufacturers rely on a single shared provider of powder, Kuraray Noritake’s zirconia materials are unique in that they are produced in an end-to-end in-house process. From the proprietary powder technology through to disc pressing and pre-sintering, KATANA™ Zirconia is produced to ensure unparalleled purity and unmatched quality.
Multilayered technology
Three of the four types of KATANA™ Zirconia—UTML, STML and HTML—incorporate Kuraray Noritake’s original multilayered build-up technology. This innovative four-layer structure faithfully replicates the translucency and colour gradation of natural dentition, resulting in an eye-pleasing final restoration. Furthermore, each member of the KATANA™ Zirconia series possesses different translucency and mechanical properties, allowing clinicians to cover a wide range of anterior and posterior restorations.
A zirconia series embedded in a system of products
Thanks to Kuraray Noritake’s emphasis on research and development, the KATANA™ Zirconia family is embedded in a complete system of products for polishing, staining, glazing, porcelain veneering and cementation in order to deliver outstanding treatment outcomes.
CERABIEN™ ZR FC Paste Stain allows for the easy characterisation of full-contour zirconia restorations. Available in 27 different shades, it delivers an extremely controllable transparency that enables the creation of highly aesthetic restorations.
When cementing a zirconia restoration during the trial fitting stage, the new KATANA™ Cleaner will surely come in handy. This non-abrasive universal cleaner from Kuraray Noritake helps to remove contamination, thereby delivering the bond strength patients deserve. Its relatively low pH value of 4.5 also means that, unlike other dental cleaners, it can be used both intra-orally and extra-orally.
Of course, when finally cementing the restoration, the dentist needs to be confident that the cementation will be both reliable and durable. PANAVIA™ V5 is Kuraray Noritake’s strongest cement yet and offers unrivalled procedural simplicity and predictability. This amine-free paste is available in five different shades that have been scientifically demonstrated to exhibit less post-polymerisation colour variance than amine-based cements. For aesthetic and stable cementation, PANAVIA™ V5 is the best option.
It is clear that, with the translucent KATANA™ Zirconia series and these associated products, Kuraray Noritake has established a fully integrated system that can work for almost any prosthetic workflow. KATANA™ Zirconia is key to durable metal-free restorations.
By Dr Salvatore Scolavino and DT Francesco Napolitano
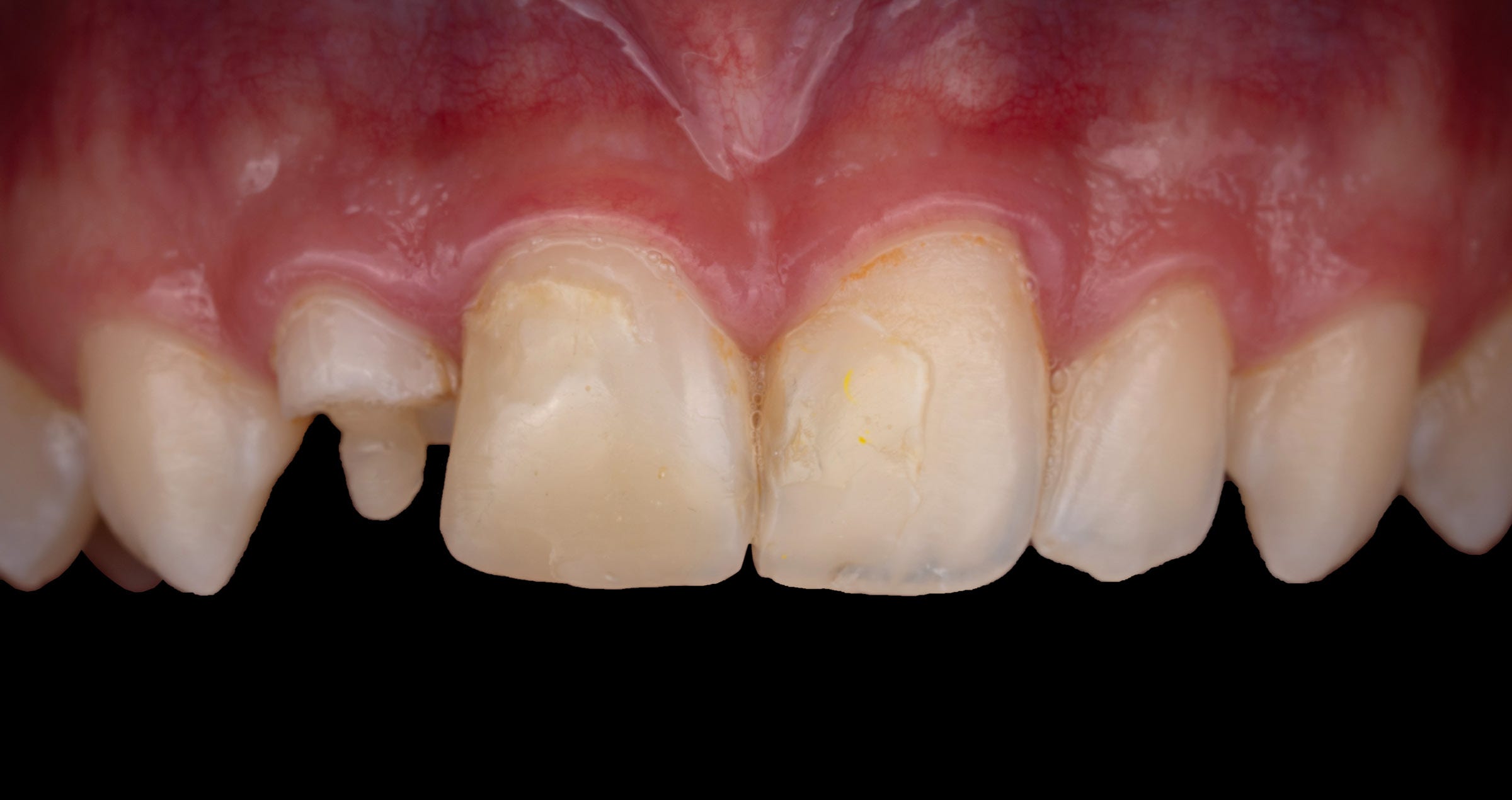
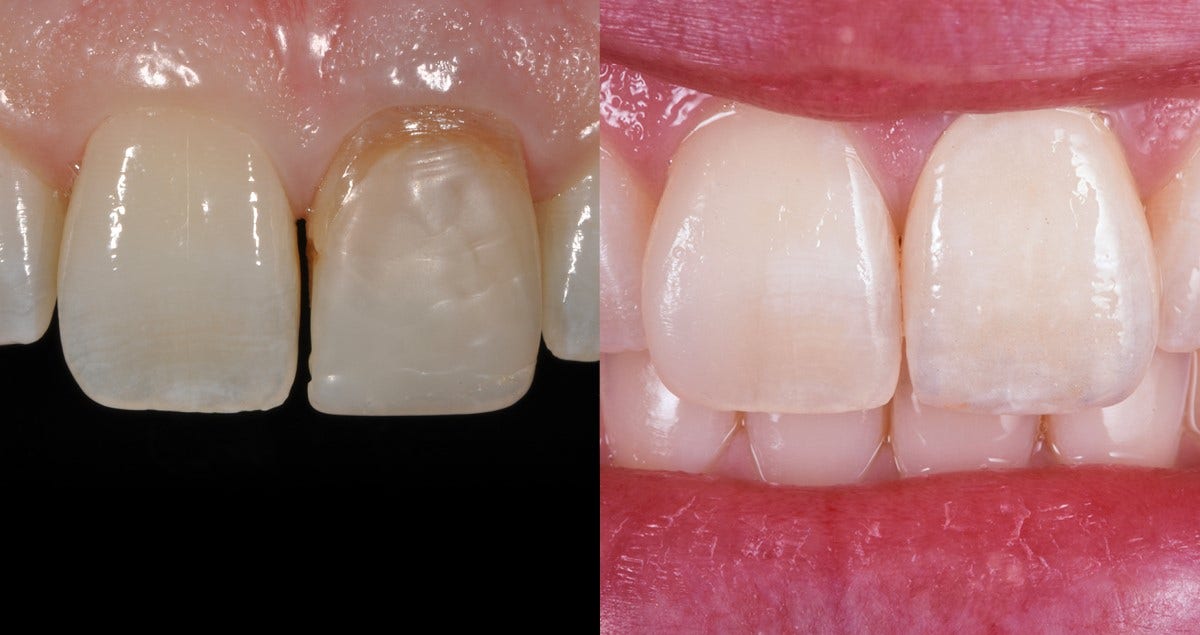
The dental laboratory is confronted with the greatest aesthetic challenge whenever it comes to the restoration of a single incisor with natural adjacent teeth. In the following case, a young patient had undergone endodontic treatment of her tooth 21 (fig. 1) while all other teeth showed their natural appearance. Tooth 21 was due for replacement now (fig. 2).
Fig. 1: X-Ray after endodontic treatment (with new crown on tooth 21 in place).
Fig. 2: The former restoration with which the patient showed up in the dentist’s practice.
To keep the natural identity, together with preserving the gingiva outline, the decision was taken in favour of a monolithic zirconia restoration, with a layered block for a full-contour crown. KATANA™ Zirconia STML (Kuraray Noritake Dental) provides for four gradational layers from „Body/Dentine“ (cervical area) to „Enamel“ (incisal aera), varying in chroma and translucency. Using this kind of milling block, it is possible to imitate the natural progression from yellowish to whitish-blue, and this in an easy manner. At the same time this way, the endodontic post wouldn’t shine through and make any aesthetic difference. On the other hand, the zirconia irradiates into the gingiva and results in a natural looking shade allover the anterior area. Furthermore for a lively and most natural-identical appeal, it was intended to individualize the crown by surface stains. With the product CZR™ FC Paste Stain by Kuraray Noritake Dental, 27 shades are available, together with fluorescence. What is essential in the front, too, is this well proven experience: All zirconia material enhances the close gingival attachment and provides for stable results of the pink-and-white aesthetics.
The dentist built up the stump 21, prepared it according to the specifications for zirconia and took the impression (fig. 3). The plaster model followed (fig. 4) and was scanned to start then the digital process. After designing, the crown was milled and tried-in at the next session with the patient (fig. 5).
Fig. 3: Impression taking after preparing tooth 21.
Fig. 4: Plaster model - the prothetic baseline of the case.
Fig. 5: Try-in of the zirconia crown in the patient’s mouth with rubber dam.
SHAPE AND COLOUR
Right when starting the case, the teeth of both jaws had been scrutinized: first for shape. Special attention was payed to the interproximale space between 11 and 21 because this area had worn out in the meantime (see again fig. 2). It was also necessary to move closer to each other the approximale margins 21/22 resp. 11/12 in their cervical-middle parts. When giving the zirconia crown its final shape, this resulted in a widely swinging outer line distally 21. For harmony reasons, tooth 11 was extended distally, too. Here, the clinician used the direct filling composite CLEARFIL MAJESTY™ Classic, shade A2 (fig. 6, 7 and 8). This nano-hybrid composite by Kuraray Noritake Dental is easy-sculpting and integrated fully with the milled crown.
It was most important for crown 21 and tooth 11 too, to create a 3D effect of the tooth structure and an age-appropriate vestibular surface texture. For this, the characteristics of the adjacent teeth and allover both jaws were examined meticulously in general and in detail. Surface burs, discs, stones, and similar instruments sophisticatedly engraved pericymatia and a groove here and there, thus accomplishing the perfect natural look.
Fig. 6: Tooth 11 before recontouring the shape distally.
Fig. 7: Finished crown 21 on the plaster model. Notice: In order to match the shape of crown 21 and close-up the margins 11/12, composite has been added in the interproximal space.
Fig. 8: Finishing the new distal outline of tooth 11.
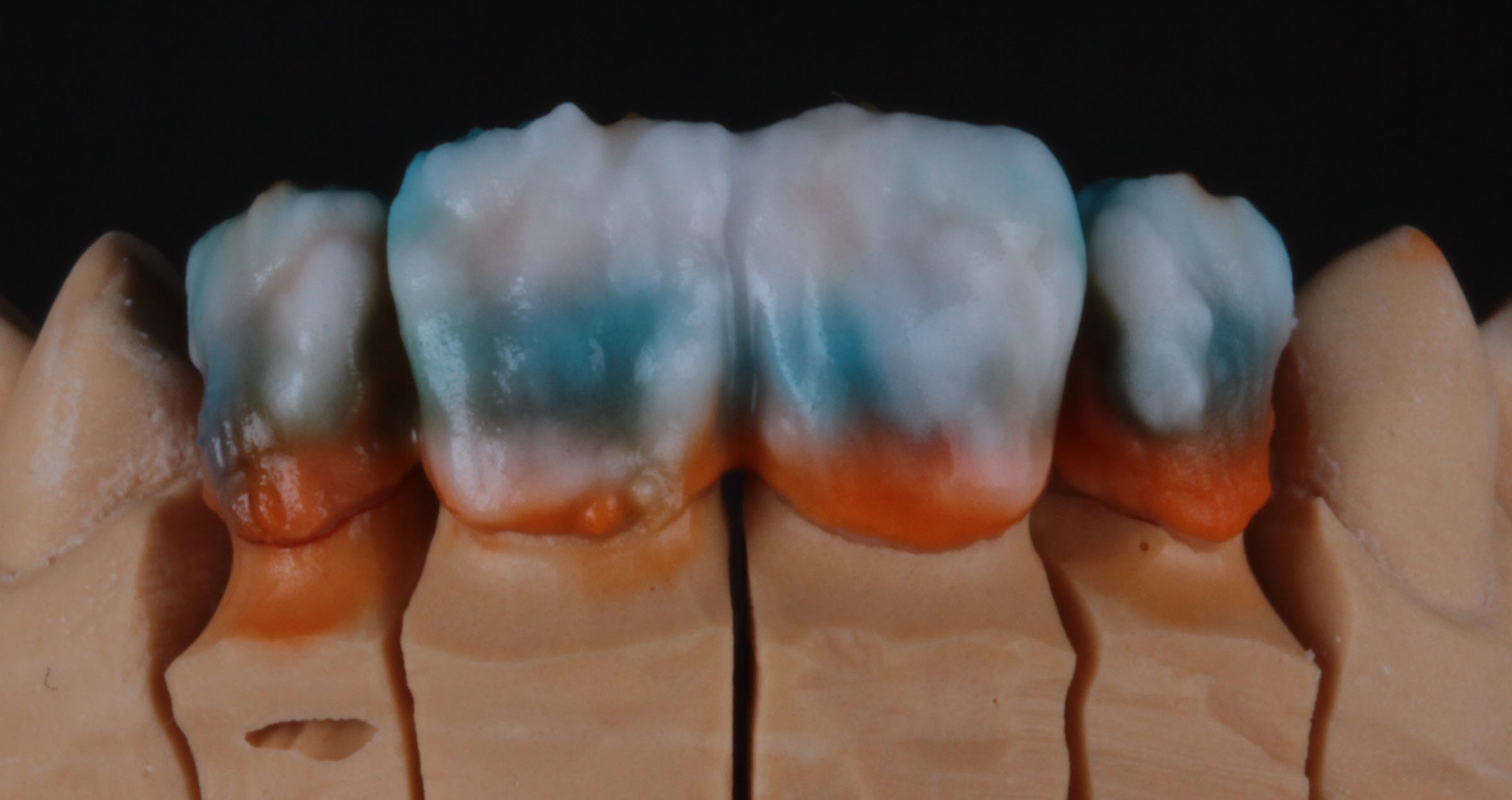
The final colour touch was given to both teeth by surface staining: with a thin layer of FC Paste Stain measuring only 50-70 micrometers in depth, different shades were applicated. The entire range was used from yellow/orange to blue and white (fig. 9a-d) in order to provoke the effect of mamelons and other structures in all thirds of the restorations.
Fig. 9a: Definitive fitting of the restoration.
Fig. 9b: Directly after the fitting.
FINAL SITUATION
Fig. 9c: View of the lips with the restoration in place.
Fig. 9d: Natural look of the upper and lower jaws.